Adding a Microsoft SQL Job
You can create a Microsoft SQL job using the context menu within the Jobs pane. You can also edit, copy and delete an existing Microsoft SQL job. If you add a Microsoft SQL job to a TA job group, items common between the job group and the Microsoft SQL job are inheritable.
However, unless the parent group has an adapter assigned to it, you must clear the Inherited option and choose an appropriate Microsoft SQL connection.
Selecting the Add MSSQL Job option from the TA Jobs pane displays the MSSql Job Definition dialog.
To add a Microsoft SQL job:
-
Click Definitions > Jobs on the Navigation pane to display the Jobs pane.
-
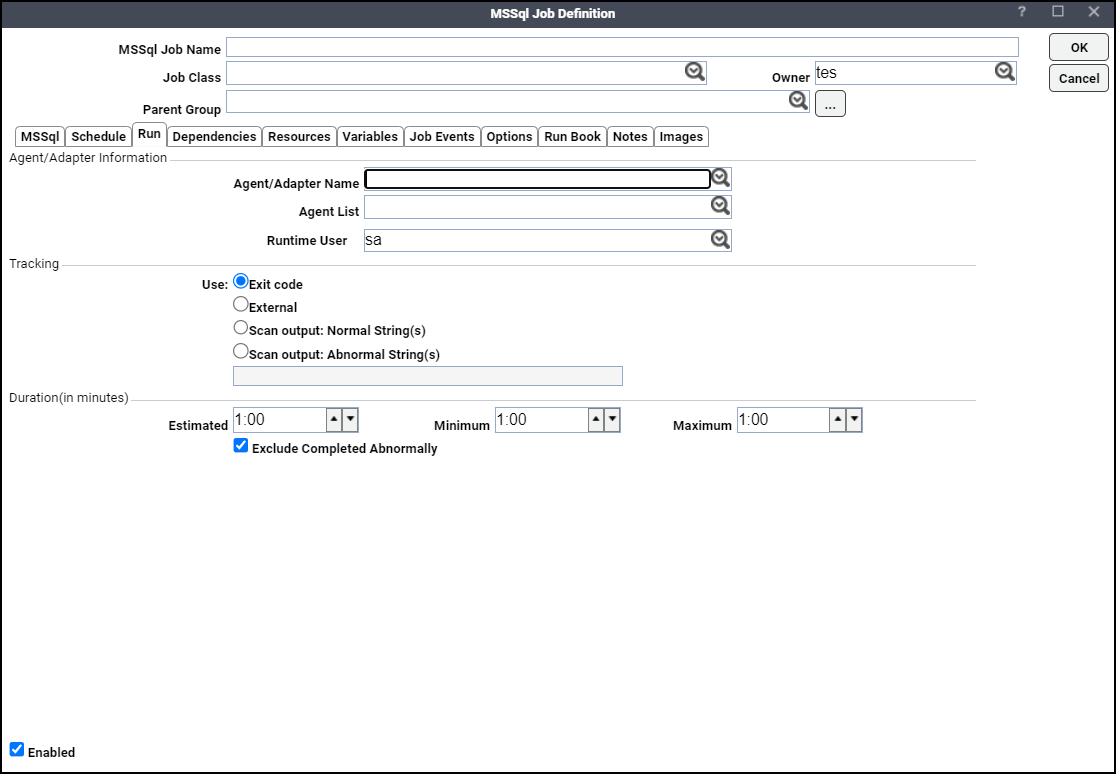
Click Add in the TA toolbar or right-click in either the Navigation or Jobs pane and click Add MSSQL Job in the context menu to display the MSSQL Job Definition dialog.
-
Click the MSSql Job Name field, and enter a name up to 50 characters in length for your job.
The Microsoft SQL Job Name is an identifier for TA only. All of the other job definition information, such as Job Class, Owner and Parent Group, is also the same as a standard TA job and is used in the same way.
If you are putting your Microsoft SQL job into a group, note that unless the parent group selected has an adapter connection assigned, you must clear the Inherited option on the Run tab before you can click a Microsoft SQL connection.
-
Click an adapter name from the Agent/Adapter Name list on the Run tab.
-
Click a runtime user from the Runtime User list.
-
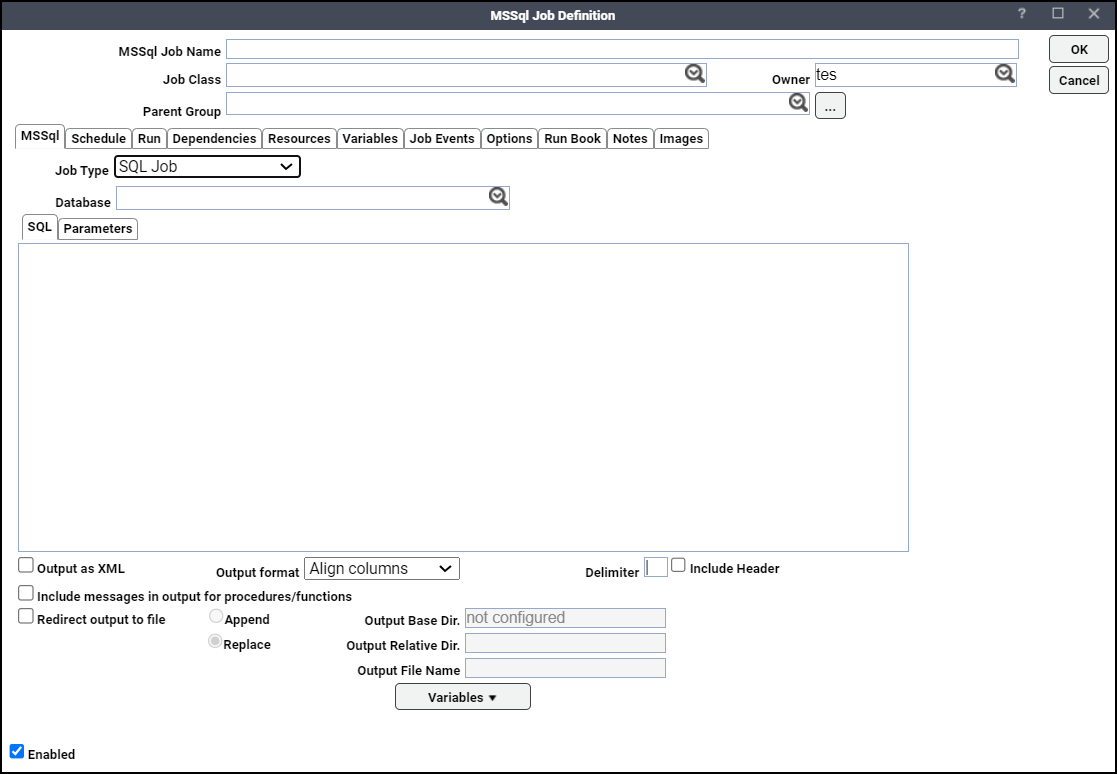
Click the MSSql tab.
-
Click the job type as SQL Job from the Type list.
-
Click the database associated with the job from the Database list.
-
Type in SQL statements to execute here (multiple statements separated by semi-colons) in the SQL tab field.
To include parameters that are replaced at runtime, use a parameter name of your choice preceded by a colon
Example: :id.
-
Click the Output as XML option to write the query results in XML format, if desired.
-
Click the Output Format list, choose how the query results are formatted, if Output as XML is not selected.
-
Align Columns – Displays the values in the most readable format.
-
CSV Format – Separates values with commas.
-
Raw – Separates values with a user-defined character.
-
-
Click the Delimiter field, specify the custom character to use for delimiting the query results, if Raw is selected for Output Format.
-
Click the Include Header option to write out the column headers of the results as well.
-
Click the Include messages in output for procedures/functions option, if you want the warning messages related to procedures/functions to be included in the job output.
-
Check the Redirect output to file checkbox if you want the job output to be stored in a file. This redirection option is independent of the Save Output Option located on the Options tab.
Example: If the Save Output Option is set to Discard and the Redirect output to file checkbox is selected, then the job output will be saved to the specified file while the Output tab on the Job Details dialog will be empty.
Example: If the Save Output Option is set to Append or Replace and the Redirect output to file checkbox is selected, the Output tab on the Job Details dialog shows the redirection message.
-
Click Append to append current output to the existing output in the output file. Click Replace to replace the existing output with current output in the output file.
The Output Base Directory field specifies the output base directory, if configured. This is a read-only field.
-
If the output base directory is not configured, the field value is shown as “not configured” in the Output Base Directory field. In this case, the job will not execute and will have the “Error Occurred” status. The corresponding error message will be shown in audit log files.
-
If the output base directory is configured, the base directory path is shown in the Output Base Directory field.
Note: Specify the path on the machine where Tidal Automation is located.
Example: Base directory path: /opt/Tidal/{adapter_guid}/, where adapter_guid is the GUID of the adapter.
Note: The base directory path is activated by specifying a value in the sysval_longstr column of the sysval “195”. This can be accomplished by executing an update statement to the database as mentioned in this example.
Example: MS SQL Query:
insert into sysval (sysval_id, sysval_longstr, sysval_lstchgtm) values (195, 'c:\temp\adapter\output', GETDATE())Example: Oracle SQL Query:
insert into sysval (sysval_id, sysval_longstr, sysval_lstchgtm) values (195, '/tmp/adapter/output', SYSDATE)Here, the sysval_longstr field contains the output base directory path. An optional sysval_integer field indicates whether the task GUID subdirectory will be appended to output base directory or not. If the value of sysval_integer is 1, the task GUID will be appended. In all other cases, the task GUID will not be appended.
Note: Restart Tidal Automation to apply the changes.
-
-
Enter the directory path relative to the output base directory in the Output Relative Directory field.
Example: Output relative directory path: relativedir/path.
-
Click the Output File Name field, enter the name of the file in which the job output is stored. This file is placed in the path resulting from step 17 and 18.
Example: If the Output File Name is specified as “sqljob.xml”, then the job output is stored in /opt/Tidal/{adapter_guid}/relativedir/path/sqljob.xml.
If you are using parameters to be replaced at runtime, click the Parameters tab view a list of parameters that have been preceded by a colon where you can provide values.
-
Click Edit to display the Variable Definition dialog.
-
Enter a parameter value, then click OK to save the value. he value displays in the variable row.
-
Click OK to save the job.